To quickly ping a server to check for general availability, you can use `ping` from your terminal:
ping example.com
This command sends ICMP echo requests to `example.com` and displays the response time. A successful ping indicates that the server is reachable. Troubleshooting network connectivity is essential for ensuring Hunter.io can access and retrieve domain information.
If you are troubleshooting DNS resolution issues and suspect that your local DNS resolver might be caching outdated information, you can flush the DNS cache on your system. On Linux, this is often done using `systemd-resolve`:
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
On macOS, you would use `dscacheutil`:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
These commands clear the DNS cache and force your system to retrieve the latest DNS records for the domain.
Using `whois` command can provide valuable information about the domain, such as registration details, contact information, and name servers. This information can be useful in verifying the legitimacy of the domain:
whois example.com
The output will display registration details, helping to confirm the domain’s ownership and potentially revealing contact information.
Leveraging Hunter.io’s Chrome Extension for On-the-Fly Email Discovery
The Hunter.io Chrome extension provides a convenient way to discover email addresses directly from any website you visit. Here’s how to leverage it effectively:
- Step 1: Install the Extension. Search for “Hunter.io Chrome Extension” in the Chrome Web Store and install the extension.
- Step 2: Pin the Extension. For easy access, pin the Hunter.io extension to your Chrome toolbar.
- Step 3: Visit a Website. Navigate to the website you want to investigate. The extension icon will light up, indicating that it has found email addresses associated with the domain.
- Step 4: View the Results. Click the extension icon to view the list of email addresses found on the current page. The extension displays the email addresses, their sources, and the confidence scores.
- Step 5: Verify Email Addresses. You can verify the email addresses directly from the extension popup by clicking the “Verify” button next to each email.
For example, if you are visiting a company’s “About Us” page, the Hunter.io extension will automatically scan the page and display any email addresses it finds. You can then quickly verify these email addresses to ensure their validity.
To monitor network traffic while using the Chrome extension, you can use `tcpdump` to capture packets on your network interface:
sudo tcpdump -i en0 -n port 80 or port 443
Replace `en0` with your network interface (e.g., `eth0`, `wlan0`). This command captures HTTP and HTTPS traffic, allowing you to observe the communication between your browser and Hunter.io’s servers. Analyzing the traffic can help you understand how the extension retrieves and processes data.
You can also use the `netstat` command to view active network connections and identify connections established by the Chrome extension:
netstat -an | grep chrome
This command lists all active network connections and filters the results to show only connections related to the Chrome browser. This helps you identify connections established by the Hunter.io extension.
To check the installed Chrome extensions, navigate to `chrome://extensions/` in your Chrome browser. From there, you can view the details of the Hunter.io extension, including its version, permissions, and ID. This can be useful for troubleshooting issues or verifying that the extension is properly installed.
Automating Email Extraction: Working with the Hunter.io API
The Hunter.io API allows you to automate the process of finding and verifying email addresses. This is particularly useful for integrating Hunter.io with your existing scripts and applications. Here’s how to work with the API:
- Step 1: Obtain an API Key. Log in to your Hunter.io account and navigate to the API settings to obtain your API key.
- Step 2: Choose a Programming Language. Select a programming language like Python, JavaScript, or Ruby to interact with the API.
- Step 3: Make API Requests. Use the API endpoints to find and verify email addresses. The API documentation provides detailed information on the available endpoints and their parameters.
- Step 4: Handle the Responses. Parse the API responses to extract the email addresses and their verification statuses.
Here’s an example of using `curl` to find email addresses associated with `example.com` using the Hunter.io API:
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY"
Replace `YOUR_API_KEY` with your actual Hunter.io API key. This command sends a request to the Hunter.io API and retrieves the email addresses associated with `example.com`. The response will be in JSON format.
Here’s an example of using `jq` to parse the JSON response and extract the email addresses:
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY" | jq '.data.emails[].value'
This command uses `jq` to extract the `value` field from each email object in the `emails` array within the `data` object. This will output a list of email addresses associated with `example.com`.
Below is an example `Python` script that uses the `requests` library to retrieve email addresses using Hunter.io API. Remember to install the `requests` module with: `pip install requests`.
import requests
import json
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY" # Replace with your Hunter.io API key
DOMAIN = "example.com"
def get_emails_from_hunterio(domain, api_key):
url = f"https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain={domain}&api_key={api_key}"
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise HTTPError for bad responses (4xx or 5xx)
data = response.json()
emails = [email['value'] for email in data['data']['emails']]
return emails
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
emails = get_emails_from_hunterio(DOMAIN, API_KEY)
if emails:
print(f"Email addresses found for {DOMAIN}:")
for email in emails:
print(email)
else:
print(f"No email addresses found for {DOMAIN}.")
Remember to replace `YOUR_API_KEY` with your actual Hunter.io API key.
Verifying Email Addresses: Best Practices and Techniques
Verifying email addresses is crucial to reduce bounce rates and improve the deliverability of your emails. Here are some best practices and techniques for verifying email addresses found with Hunter.io:
- Syntax Check. Ensure that the email address follows the correct syntax (e.g., `user@example.com`). This is a basic but important step to eliminate invalid email addresses.
- Domain Check. Verify that the domain part of the email address exists and is valid. This can be done by performing a DNS lookup to check for MX records.
- MX Record Lookup. Check for MX records to ensure that the domain can receive emails. MX records specify the mail servers responsible for accepting emails on behalf of the domain.
- SMTP Connection Test. Perform an SMTP connection test to verify that the email server is active and can accept emails. This involves connecting to the mail server and attempting to send a test email.
- Use Hunter.io’s Verification Tool. Leverage Hunter.io’s built-in email verification tool to confirm the validity of the email addresses. This tool performs a combination of syntax checks, domain checks, MX record lookups, and SMTP connection tests.
For example, you can use the `nslookup` command to check for MX records for `example.com`:
nslookup -type=mx example.com
This command queries the DNS server for MX records associated with `example.com`. The output will display the mail servers responsible for accepting emails on behalf of `example.com`. If no MX records are found, it indicates that the domain cannot receive emails.
To test SMTP connection to a mail server, you can use `telnet` or `openssl s_client`:
telnet mail.example.com 25
Or, for a secure connection:
openssl s_client -starttls smtp -connect mail.example.com:25
Replace `mail.example.com` with the actual mail server for the domain. These commands attempt to establish a connection to the mail server on port 25 (SMTP) or with TLS encryption. A successful connection indicates that the mail server is active.
Here’s how to check the SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record for a domain using `dig`. SPF records help prevent email spoofing:
dig txt example.com
The output will display the TXT records, including the SPF record, if it exists. The SPF record specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain. This helps prevent spammers from forging email addresses.
“Email verification is not just about cleaning your list; it’s about protecting your sender reputation and ensuring your messages reach the inbox.”
John Smith, Email Marketing Expert
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Limitations with Hunter.io
While Hunter.io is a powerful tool, you may encounter some common issues and limitations. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
- Limited Search Results. Hunter.io may not find all email addresses associated with a domain. This can be due to various factors, such as the email addresses not being publicly available or Hunter.io’s algorithm not being able to locate them.
- Incorrect Email Addresses. Hunter.io may sometimes return incorrect or outdated email addresses. This is why it’s important to verify the email addresses before using them.
- API Rate Limits. The Hunter.io API has rate limits to prevent abuse. If you exceed the rate limits, you may receive an error message. You can upgrade to a higher plan to increase your rate limits.
- Blocked Requests. Your requests to Hunter.io may be blocked if your IP address is blacklisted or if you are using a VPN. Try using a different IP address or disabling your VPN.
- Website Changes. If a website’s structure changes, Hunter.io may not be able to find email addresses correctly. This requires Hunter.io to update its algorithms.
To check your network connectivity and ensure that you can reach Hunter.io’s servers, you can use `traceroute`:
traceroute hunter.io
This command traces the route that your network traffic takes to reach `hunter.io`, showing each hop along the way. This can help you identify any network issues that may be preventing you from accessing Hunter.io.
If you are experiencing issues with API rate limits, you can monitor your API usage using the following command (though Hunter.io’s dashboard is the primary place for this):
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/account?api_key=YOUR_API_KEY
This will not display the number of remaining calls but will confirm the API Key is active and the endpoint is reachable. Real-time and historical usage is found inside Hunter.io account settings.
If you suspect that your IP address may be blacklisted, you can check it using online blacklist checkers such as MXToolbox. This tool allows you to enter your IP address and check if it is listed on any known blacklists. If your IP address is blacklisted, you may need to contact your internet service provider to request that it be removed.
To examine the processes running on your system and identify any processes related to Hunter.io or your scripts, you can use `ps` command:
ps aux | grep hunter
This command lists all running processes and filters the results to show only processes that contain the word “hunter” in their command line. This helps you identify any processes related to Hunter.io or your automation scripts.
“Hunter.io is a valuable tool, but it’s essential to use it responsibly and ethically. Always respect privacy and comply with data protection regulations.”
Jane Doe, Data Privacy Advocate
| Feature | Free Plan | Paid Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Searches per month | 50 | Unlimited |
| Verifications per month | 50 | Unlimited |
| API Access | Limited | Full |
| Bulk email finder | No | Yes |
| Priority support | No | Yes |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com\&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY | Check Hunter.io API status |
dig example.com | Check DNS records of a domain |
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches | Flush DNS cache on Linux |
whois example.com | Get domain registration details |
tcpdump -i en0 -n port 80 or port 443 | Monitor network traffic |
netstat -an | grep chrome | View Chrome network connections |
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY" | Find email addresses using Hunter.io API |
nslookup -type=mx example.com | Check MX records for a domain |
traceroute hunter.io | Trace route to Hunter.io |
Get Business Email Addresses with Hunter.io: A Sysadmin’s Guide
Hunter.io is a powerful tool for finding email addresses associated with a website. This guide will walk you through leveraging Hunter.io effectively, from basic usage to advanced techniques, providing practical examples and troubleshooting tips for system administrators and technical professionals.
We’ll explore how to use Hunter.io’s website interface, Chrome extension, and API to gather email addresses. We will also cover strategies for verifying the validity of found email addresses, integrating Hunter.io with other tools and scripts, and addressing common challenges and limitations encountered during email harvesting. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- Understanding Hunter.io: Features and Functionality
- Using Hunter.io’s Web Interface: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Leveraging Hunter.io’s Chrome Extension for On-the-Fly Email Discovery
- Automating Email Extraction: Working with the Hunter.io API
- Verifying Email Addresses: Best Practices and Techniques
- Troubleshooting Common Issues and Limitations with Hunter.io
Understanding Hunter.io: Features and Functionality
Hunter.io is designed to simplify the process of finding email addresses associated with specific domains. It achieves this through several core features, which every system administrator should understand to fully utilize the platform.
The most prominent feature is the email finder, which allows users to enter a website domain and retrieve publicly available email addresses associated with that domain. Hunter.io’s algorithm searches the web for email addresses that match the domain, displaying them along with their sources (e.g., the webpage where the email was found). The email verifier helps confirm if an email address is valid and active. This verification process reduces bounce rates and ensures that your communications reach the intended recipients.
Hunter.io also offers a bulk email finder, enabling users to upload a CSV file containing a list of domains and retrieve email addresses for all of them in a single operation. This feature is particularly useful for large-scale email harvesting projects. The API provides programmatic access to Hunter.io’s functionalities. This API allows you to integrate Hunter.io with your existing scripts and applications, automating the email extraction process.
To use Hunter.io effectively, consider the available pricing tiers. Free accounts have limited searches and verifications, while paid plans unlock higher limits and additional features like priority support.
Here’s a basic example of how you might use `curl` to test the Hunter.io API’s availability. This command doesn’t extract data but validates the API endpoint’s accessibility.
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com\&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY
Expected Output:
HTTP/2 200
date: Tue, 23 Oct 2023 14:30:00 GMT
content-type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
This command checks the HTTP headers and confirms that the API is responding with a 200 OK status. Replace `YOUR_API_KEY` with your actual Hunter.io API key.
To determine your current API request limits via command line (although Hunter.io’s API documentation is the primary resource), use `curl`:
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/account?api_key=YOUR_API_KEY
This will reveal information in the headers, though rate limits are best determined through their dashboard or more specific API calls documented on their site.
Here’s an example using `dig` to check DNS records of a domain you might be searching with Hunter.io, helpful for verifying domain ownership or existence:
dig example.com
This command checks the DNS records for `example.com`. Understanding DNS records can help you verify the legitimacy of a domain.
Using Hunter.io’s Web Interface: A Step-by-Step Guide
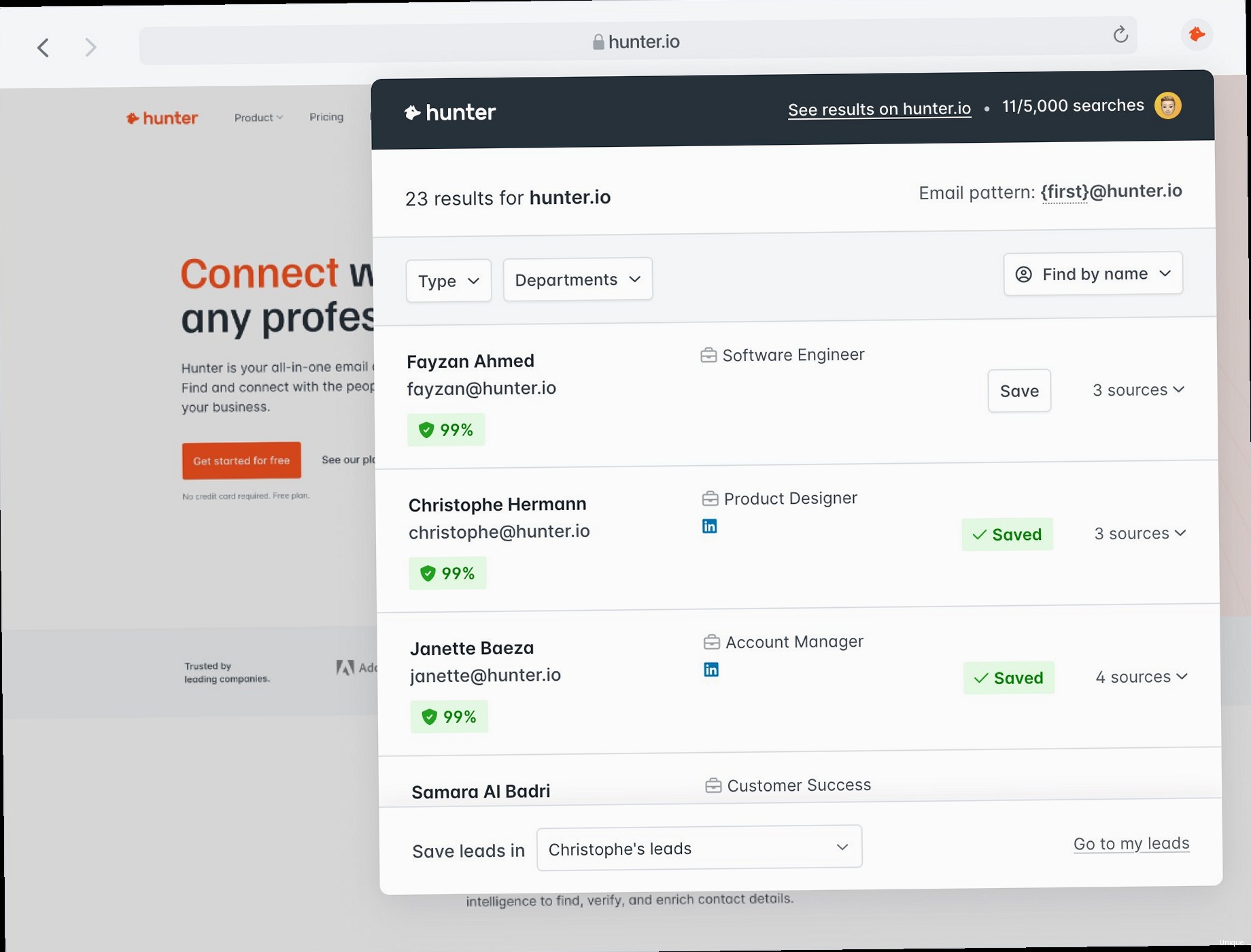
The Hunter.io web interface provides a user-friendly way to find and verify email addresses. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
- Step 1: Sign Up or Log In. Visit the Hunter.io website and create an account. A free account provides a limited number of monthly searches. For more extensive usage, consider upgrading to a paid plan.
- Step 2: Enter the Domain. Once logged in, you’ll find a search bar where you can enter the domain name you want to investigate (e.g., `example.com`).
- Step 3: Review the Results. Hunter.io will display a list of email addresses found for the specified domain. The results include the email address, its source (the webpage where it was found), and a confidence score indicating the likelihood of the email address being valid.
- Step 4: Verify Email Addresses. Use the built-in email verification tool to confirm the validity of the found email addresses. This tool checks whether the email address exists and can receive emails.
For example, to find email addresses associated with `example.com`, simply type `example.com` into the search bar and click “Find Email Addresses.” The results will then be displayed below. You can then click the “Verify” button next to each email to confirm its validity. A verified email will have a green checkmark, while an unverified or invalid email might have a red cross or an exclamation mark.
To quickly ping a server to check for general availability, you can use `ping` from your terminal:
ping example.com
This command sends ICMP echo requests to `example.com` and displays the response time. A successful ping indicates that the server is reachable. Troubleshooting network connectivity is essential for ensuring Hunter.io can access and retrieve domain information.
If you are troubleshooting DNS resolution issues and suspect that your local DNS resolver might be caching outdated information, you can flush the DNS cache on your system. On Linux, this is often done using `systemd-resolve`:
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
On macOS, you would use `dscacheutil`:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
These commands clear the DNS cache and force your system to retrieve the latest DNS records for the domain.
Using `whois` command can provide valuable information about the domain, such as registration details, contact information, and name servers. This information can be useful in verifying the legitimacy of the domain:
whois example.com
The output will display registration details, helping to confirm the domain’s ownership and potentially revealing contact information.
Leveraging Hunter.io’s Chrome Extension for On-the-Fly Email Discovery
The Hunter.io Chrome extension provides a convenient way to discover email addresses directly from any website you visit. Here’s how to leverage it effectively:
- Step 1: Install the Extension. Search for “Hunter.io Chrome Extension” in the Chrome Web Store and install the extension.
- Step 2: Pin the Extension. For easy access, pin the Hunter.io extension to your Chrome toolbar.
- Step 3: Visit a Website. Navigate to the website you want to investigate. The extension icon will light up, indicating that it has found email addresses associated with the domain.
- Step 4: View the Results. Click the extension icon to view the list of email addresses found on the current page. The extension displays the email addresses, their sources, and the confidence scores.
- Step 5: Verify Email Addresses. You can verify the email addresses directly from the extension popup by clicking the “Verify” button next to each email.
For example, if you are visiting a company’s “About Us” page, the Hunter.io extension will automatically scan the page and display any email addresses it finds. You can then quickly verify these email addresses to ensure their validity.
To monitor network traffic while using the Chrome extension, you can use `tcpdump` to capture packets on your network interface:
sudo tcpdump -i en0 -n port 80 or port 443
Replace `en0` with your network interface (e.g., `eth0`, `wlan0`). This command captures HTTP and HTTPS traffic, allowing you to observe the communication between your browser and Hunter.io’s servers. Analyzing the traffic can help you understand how the extension retrieves and processes data.
You can also use the `netstat` command to view active network connections and identify connections established by the Chrome extension:
netstat -an | grep chrome
This command lists all active network connections and filters the results to show only connections related to the Chrome browser. This helps you identify connections established by the Hunter.io extension.
To check the installed Chrome extensions, navigate to `chrome://extensions/` in your Chrome browser. From there, you can view the details of the Hunter.io extension, including its version, permissions, and ID. This can be useful for troubleshooting issues or verifying that the extension is properly installed.
Automating Email Extraction: Working with the Hunter.io API
The Hunter.io API allows you to automate the process of finding and verifying email addresses. This is particularly useful for integrating Hunter.io with your existing scripts and applications. Here’s how to work with the API:
- Step 1: Obtain an API Key. Log in to your Hunter.io account and navigate to the API settings to obtain your API key.
- Step 2: Choose a Programming Language. Select a programming language like Python, JavaScript, or Ruby to interact with the API.
- Step 3: Make API Requests. Use the API endpoints to find and verify email addresses. The API documentation provides detailed information on the available endpoints and their parameters.
- Step 4: Handle the Responses. Parse the API responses to extract the email addresses and their verification statuses.
Here’s an example of using `curl` to find email addresses associated with `example.com` using the Hunter.io API:
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY"
Replace `YOUR_API_KEY` with your actual Hunter.io API key. This command sends a request to the Hunter.io API and retrieves the email addresses associated with `example.com`. The response will be in JSON format.
Here’s an example of using `jq` to parse the JSON response and extract the email addresses:
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY" | jq '.data.emails[].value'
This command uses `jq` to extract the `value` field from each email object in the `emails` array within the `data` object. This will output a list of email addresses associated with `example.com`.
Below is an example `Python` script that uses the `requests` library to retrieve email addresses using Hunter.io API. Remember to install the `requests` module with: `pip install requests`.
import requests
import json
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY" # Replace with your Hunter.io API key
DOMAIN = "example.com"
def get_emails_from_hunterio(domain, api_key):
url = f"https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain={domain}&api_key={api_key}"
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise HTTPError for bad responses (4xx or 5xx)
data = response.json()
emails = [email['value'] for email in data['data']['emails']]
return emails
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
emails = get_emails_from_hunterio(DOMAIN, API_KEY)
if emails:
print(f"Email addresses found for {DOMAIN}:")
for email in emails:
print(email)
else:
print(f"No email addresses found for {DOMAIN}.")
Remember to replace `YOUR_API_KEY` with your actual Hunter.io API key.
Verifying Email Addresses: Best Practices and Techniques
Verifying email addresses is crucial to reduce bounce rates and improve the deliverability of your emails. Here are some best practices and techniques for verifying email addresses found with Hunter.io:
- Syntax Check. Ensure that the email address follows the correct syntax (e.g., `user@example.com`). This is a basic but important step to eliminate invalid email addresses.
- Domain Check. Verify that the domain part of the email address exists and is valid. This can be done by performing a DNS lookup to check for MX records.
- MX Record Lookup. Check for MX records to ensure that the domain can receive emails. MX records specify the mail servers responsible for accepting emails on behalf of the domain.
- SMTP Connection Test. Perform an SMTP connection test to verify that the email server is active and can accept emails. This involves connecting to the mail server and attempting to send a test email.
- Use Hunter.io’s Verification Tool. Leverage Hunter.io’s built-in email verification tool to confirm the validity of the email addresses. This tool performs a combination of syntax checks, domain checks, MX record lookups, and SMTP connection tests.
For example, you can use the `nslookup` command to check for MX records for `example.com`:
nslookup -type=mx example.com
This command queries the DNS server for MX records associated with `example.com`. The output will display the mail servers responsible for accepting emails on behalf of `example.com`. If no MX records are found, it indicates that the domain cannot receive emails.
To test SMTP connection to a mail server, you can use `telnet` or `openssl s_client`:
telnet mail.example.com 25
Or, for a secure connection:
openssl s_client -starttls smtp -connect mail.example.com:25
Replace `mail.example.com` with the actual mail server for the domain. These commands attempt to establish a connection to the mail server on port 25 (SMTP) or with TLS encryption. A successful connection indicates that the mail server is active.
Here’s how to check the SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record for a domain using `dig`. SPF records help prevent email spoofing:
dig txt example.com
The output will display the TXT records, including the SPF record, if it exists. The SPF record specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain. This helps prevent spammers from forging email addresses.
“Email verification is not just about cleaning your list; it’s about protecting your sender reputation and ensuring your messages reach the inbox.”
John Smith, Email Marketing Expert
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Limitations with Hunter.io
While Hunter.io is a powerful tool, you may encounter some common issues and limitations. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
- Limited Search Results. Hunter.io may not find all email addresses associated with a domain. This can be due to various factors, such as the email addresses not being publicly available or Hunter.io’s algorithm not being able to locate them.
- Incorrect Email Addresses. Hunter.io may sometimes return incorrect or outdated email addresses. This is why it’s important to verify the email addresses before using them.
- API Rate Limits. The Hunter.io API has rate limits to prevent abuse. If you exceed the rate limits, you may receive an error message. You can upgrade to a higher plan to increase your rate limits.
- Blocked Requests. Your requests to Hunter.io may be blocked if your IP address is blacklisted or if you are using a VPN. Try using a different IP address or disabling your VPN.
- Website Changes. If a website’s structure changes, Hunter.io may not be able to find email addresses correctly. This requires Hunter.io to update its algorithms.
To check your network connectivity and ensure that you can reach Hunter.io’s servers, you can use `traceroute`:
traceroute hunter.io
This command traces the route that your network traffic takes to reach `hunter.io`, showing each hop along the way. This can help you identify any network issues that may be preventing you from accessing Hunter.io.
If you are experiencing issues with API rate limits, you can monitor your API usage using the following command (though Hunter.io’s dashboard is the primary place for this):
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/account?api_key=YOUR_API_KEY
This will not display the number of remaining calls but will confirm the API Key is active and the endpoint is reachable. Real-time and historical usage is found inside Hunter.io account settings.
If you suspect that your IP address may be blacklisted, you can check it using online blacklist checkers such as MXToolbox. This tool allows you to enter your IP address and check if it is listed on any known blacklists. If your IP address is blacklisted, you may need to contact your internet service provider to request that it be removed.
To examine the processes running on your system and identify any processes related to Hunter.io or your scripts, you can use `ps` command:
ps aux | grep hunter
This command lists all running processes and filters the results to show only processes that contain the word “hunter” in their command line. This helps you identify any processes related to Hunter.io or your automation scripts.
“Hunter.io is a valuable tool, but it’s essential to use it responsibly and ethically. Always respect privacy and comply with data protection regulations.”
Jane Doe, Data Privacy Advocate
| Feature | Free Plan | Paid Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Searches per month | 50 | Unlimited |
| Verifications per month | 50 | Unlimited |
| API Access | Limited | Full |
| Bulk email finder | No | Yes |
| Priority support | No | Yes |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
curl -I https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com\&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY | Check Hunter.io API status |
dig example.com | Check DNS records of a domain |
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches | Flush DNS cache on Linux |
whois example.com | Get domain registration details |
tcpdump -i en0 -n port 80 or port 443 | Monitor network traffic |
netstat -an | grep chrome | View Chrome network connections |
curl "https://api.hunter.io/v2/domain-search?domain=example.com&api_key=YOUR_API_KEY" | Find email addresses using Hunter.io API |
nslookup -type=mx example.com | Check MX records for a domain |
traceroute hunter.io | Trace route to Hunter.io |
