
How to Start Cold Emailing: A Practical Guide to Getting Results
Cold emailing, when done correctly, can be a powerful tool for generating leads, building connections, and driving sales. This guide provides a practical, step-by-step approach to launching effective cold email campaigns, covering everything from defining your target audience to crafting compelling messaging and optimizing for deliverability. Learn how to cut through the noise and land your emails in the inbox, not the spam folder.
Table of Contents
- Defining Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
- Crafting Compelling and Personalized Emails
- Setting Up Your Email Infrastructure for Deliverability
- Finding and Verifying Email Addresses
- Tracking and Optimizing Your Cold Email Campaigns
Defining Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)

- Industry: Which industries benefit most from your product or service? Focus on industries where you have a proven track record of success.
- Company Size: Are you targeting startups, SMEs, or large enterprises? Consider factors like budget, decision-making process, and implementation complexity.
- Job Title/Role: Who is the decision-maker or influencer you need to reach? Understand their responsibilities and how your offering can help them achieve their goals.
- Geography: Is your target market local, national, or global? Consider language, cultural nuances, and time zones.
- Technology Stack: What technologies are they already using? This can help you understand their needs and tailor your messaging.
- Pain Points: What are the specific challenges they face? Are they struggling with efficiency, cost, security, or compliance?
- Goals: What are they trying to achieve? Are they looking to increase revenue, reduce costs, improve efficiency, or enhance customer satisfaction?
- Motivations: What motivates them in their role? Are they driven by career advancement, recognition, or a desire to make a positive impact?
“The more specific you are with your ICP, the more effective your cold email campaigns will be. Don’t try to be everything to everyone.”
– Cold Email Expert
Crafting Compelling and Personalized Emails
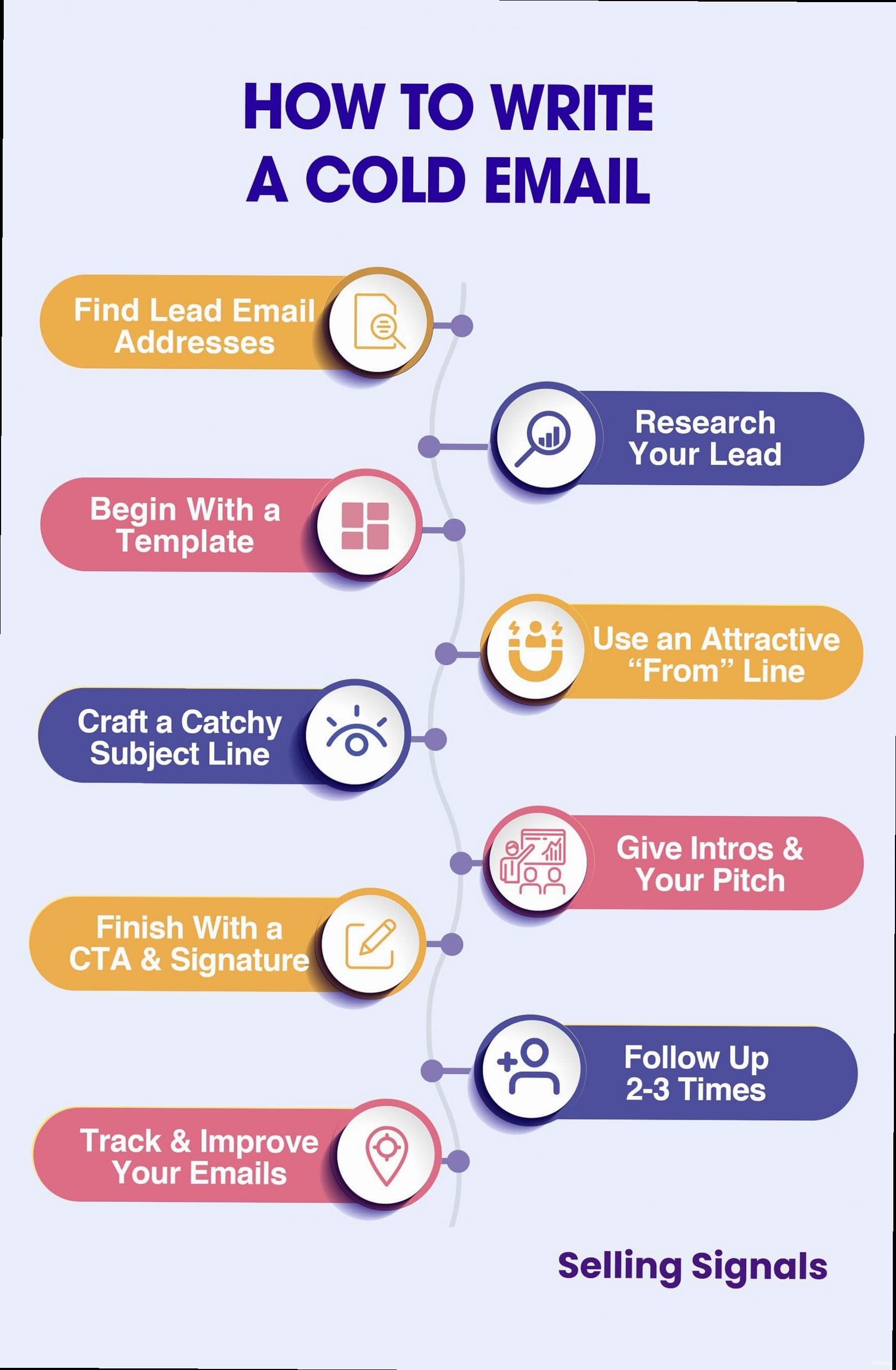
- Keep it Short: Aim for under 50 characters to ensure it displays properly on mobile devices.
- Personalize: Use the recipient’s name or company name if possible.
- Intrigue: Ask a question or highlight a specific benefit.
- Avoid Spam Trigger Words: Words like “free,” “urgent,” and “guaranteed” can trigger spam filters.
- “Quick question for [Name] at [Company]”
- “Improving project efficiency at [Company]”
- “[Name], struggling with [Pain Point]?”
- “A better way to manage projects at [Company]”
- Reference Their Website: “I noticed on your website that you’re using [Technology]. We can help you optimize it.”
- Mention a Recent Blog Post: “I enjoyed your recent article on [Topic]. It resonated with me because…”
- Congratulate Them on an Achievement: “Congratulations on your recent funding round. I’m impressed with your growth.”
- Mention a Mutual Connection: “I saw that you’re connected with [Mutual Connection] on LinkedIn. We worked together on [Project].”
- “Hi [Name], I saw that [Company] recently launched a new product line. Congratulations!”
- “Hi [Name], I was impressed with your presentation at [Conference] on [Topic].”
- “Hi [Name], I noticed you’re using Jira for project management. We have a tool that integrates seamlessly with it.”
- Focus on Benefits: Highlight the benefits of your offering, not just the features.
- Quantify Your Value: Use numbers to demonstrate the impact you can have.
- Keep it Concise: Get straight to the point and avoid jargon.
- Make it Easy to Respond: Offer a clear call to action, such as scheduling a call or visiting your website.
- “We can help you improve your project efficiency by 20% with our project management tool. Would you be open to a quick 15-minute call to discuss your needs?”
- “Our cybersecurity consulting services can help you protect your sensitive data and comply with regulations. Would you like to schedule a free security assessment?”
- “We’ve helped similar companies like [Competitor] reduce their marketing costs by 30% with our lead generation platform. Can we show you how?”
Subject: Quick question for [Name] at [Company]
Hi [Name],
I saw that [Company] recently launched a new product line. Congratulations!
I'm reaching out because we help software development companies like yours improve project efficiency by 20% with our project management tool.
Would you be open to a quick 15-minute call to discuss your needs?
Best regards,
[Your Name]
Setting Up Your Email Infrastructure for Deliverability
Even the most compelling email will be ineffective if it never reaches the recipient’s inbox. Ensuring email deliverability is a critical aspect of cold emailing. Email providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo use sophisticated algorithms to filter out spam. To avoid being flagged as spam, you need to set up your email infrastructure correctly and follow best practices for sending emails. This involves configuring SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, warming up your IP address, and maintaining a good sender reputation. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) SPF is a DNS record that specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. This helps prevent spammers from forging your email address and sending malicious emails. Configuration: Add an SPF record to your domain’s DNS settings. The SPF record should include the IP addresses of your mail servers and any third-party services you use to send emails.v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.0/24 ip4:198.51.100.0/24 include:_spf.google.com ~all
v=spf1: Specifies the SPF version.ip4:192.0.2.0/24: Authorizes the IP address range 192.0.2.0/24 to send emails.ip4:198.51.100.0/24: Authorizes the IP address range 198.51.100.0/24 to send emails.include:_spf.google.com: Authorizes Google’s mail servers to send emails on behalf of your domain (if you’re using Google Workspace).~all: Specifies a soft fail, meaning that emails from unauthorized servers will be accepted but marked as suspicious. A hard fail (-all) will reject emails from unauthorized servers. It’s generally recommended to start with a soft fail and then switch to a hard fail once you’re confident that your SPF record is configured correctly.
google._domainkey.example.com. 3600 IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA7Z...long_public_key...IDAQAB"
google._domainkey.example.com: The DKIM selector (in this case, “google”) and your domain name.3600 IN TXT: Specifies that this is a TXT record with a TTL of 3600 seconds."v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA7Z...long_public_key...IDAQAB": The DKIM record value, including the version (v=DKIM1), the key type (k=rsa), and the public key (p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA7Z...long_public_key...IDAQAB).
_dmarc.example.com. 3600 IN TXT "v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@example.com; ruf=mailto:forensic@example.com; adkim=r; aspf=r; rf=afrf1"
v=DMARC1: Specifies the DMARC version.p=none: Specifies the policy to be applied to emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks.nonemeans that email providers should take no action. Other options includequarantine(move the email to the spam folder) andreject(reject the email). It’s generally recommended to start withp=noneand then gradually move top=quarantineandp=rejectas you gain more confidence in your DMARC configuration.rua=mailto:dmarc@example.com: Specifies the email address to which aggregate reports should be sent. These reports provide a summary of email authentication activity.ruf=mailto:forensic@example.com: Specifies the email address to which forensic reports should be sent. These reports provide detailed information about individual emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks.adkim=randaspf=r: Specifies the alignment mode for DKIM and SPF.rmeans that relaxed alignment should be used, whilesmeans that strict alignment should be used.rf=afrf1: Specifies the report format.
| Day | Emails Sent |
|---|---|
| Day 1-3 | 50-100 |
| Day 4-7 | 100-200 |
| Day 8-14 | 200-400 |
| Day 15-30 | 400-800 |
Finding and Verifying Email Addresses
Once you have a well-defined ICP and compelling email copy, you need to find the email addresses of your target prospects. This can be a challenging task, as email addresses are not always publicly available. Furthermore, sending emails to invalid or outdated email addresses can damage your sender reputation. Therefore, it’s crucial to use reliable methods for finding email addresses and to verify their accuracy before sending any emails. LinkedIn Sales Navigator LinkedIn Sales Navigator is a powerful tool for finding and identifying potential leads. It allows you to search for prospects based on various criteria, such as industry, company size, job title, and location. While Sales Navigator doesn’t directly provide email addresses, it gives you valuable information about your prospects, which you can then use to find their email addresses through other methods. Usage: Use Sales Navigator to identify prospects who match your ICP. Pay attention to their profiles, activity, and connections. Look for clues that might help you find their email address, such as their company website, blog posts, or social media profiles. Example: Search for “Project Manager” at “Software Development” companies with “50-200 employees” in “United States.” Review the search results and identify potential leads. Email Finder Tools There are numerous email finder tools available online that can help you find email addresses based on a person’s name and company website. These tools use various techniques, such as web scraping and pattern matching, to identify potential email addresses. Examples: Hunter.io, Apollo.io, Snov.io, and FindThatLead are popular email finder tools. Usage: Enter the prospect’s name and company website into the email finder tool. The tool will then search for potential email addresses and display the results. Example: Use Hunter.io to find the email address of John Doe at example.com. Enter “John Doe” and “example.com” into Hunter.io. The tool may suggest “john.doe@example.com” as a potential email address. Email Verification Services Before sending any emails, it’s crucial to verify the accuracy of the email addresses you’ve found. Sending emails to invalid or outdated email addresses can damage your sender reputation and increase your bounce rate. Email verification services can help you identify invalid email addresses and remove them from your list. Examples: NeverBounce, ZeroBounce, and Hunter.io (also offers verification) are popular email verification services. Usage: Upload your list of email addresses to the email verification service. The service will then check each email address to determine if it’s valid. Example: Upload a CSV file containing a list of email addresses to NeverBounce. NeverBounce will then verify the email addresses and provide a report indicating which email addresses are valid, invalid, or risky. Manual Research Sometimes, the best way to find an email address is through manual research. This involves searching for the email address on the company website, blog posts, social media profiles, and other online sources. Techniques:- Check the Company Website: Look for a “Contact Us” page or an “About Us” page that might list email addresses.
- Search for Blog Posts: Check for blog posts written by the prospect. They may have included their email address in their author bio.
- Check Social Media Profiles: Check the prospect’s LinkedIn, Twitter, and other social media profiles. They may have listed their email address in their profile.
- Use Google Search Operators: Use Google search operators to search for the email address on the company website. For example, you can search for
site:example.com "john.doe@example.com".
Tracking and Optimizing Your Cold Email Campaigns
Once you’ve launched your cold email campaigns, it’s essential to track your results and optimize your campaigns for better performance. Tracking key metrics like open rates, click-through rates, reply rates, and conversion rates will provide valuable insights into what’s working and what’s not. Use this data to refine your ICP, improve your email copy, and optimize your sending schedule. Key Metrics to Track- Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who opened your email. A higher open rate indicates that your subject line is effective.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of recipients who clicked on a link in your email. A higher CTR indicates that your email copy is engaging and relevant.
- Reply Rate: The percentage of recipients who replied to your email. A higher reply rate indicates that your email copy is compelling and that your offer is attractive.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of emails that could not be delivered. A high bounce rate can damage your sender reputation.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of recipients who took the desired action, such as scheduling a call or making a purchase. A higher conversion rate indicates that your campaign is successful.
- Open Rate: 20-50% is a good range.
- Reply Rate: 1-5% is a solid benchmark.
- Bounce Rate: Keep this below 2%.
- Subject Line: Test different subject lines to see which ones generate the highest open rates.
- Opening Line: Test different opening lines to see which ones are most engaging.
- Value Proposition: Test different value propositions to see which ones resonate most with your target audience.
- Call to Action: Test different calls to action to see which ones generate the highest conversion rates.
- Email Length: Experiment with shorter and longer emails.
- Personalize the Subject Line: Use the recipient’s name or company name in the subject line.
- Personalize the Opening Line: Reference something specific about the recipient’s company or role.
- Segment Your Audience: Segment your audience based on industry, company size, job title, or other relevant criteria.
- Tailor Your Message: Tailor your message to the specific needs and interests of each segment.
Article Monster
Email marketing expert sharing insights about cold outreach, deliverability, and sales growth strategies.