How to Identify Nutrient Deficiencies in Indoor Plants?
Indoor plants require a proper balance of nutrients to thrive and stay healthy. However, sometimes they may lack essential nutrients, leading to nutrient deficiencies. Identifying these deficiencies early is crucial to ensure your plants remain vibrant and lush. Here are some tips on how to recognize nutrient deficiencies in indoor plants:
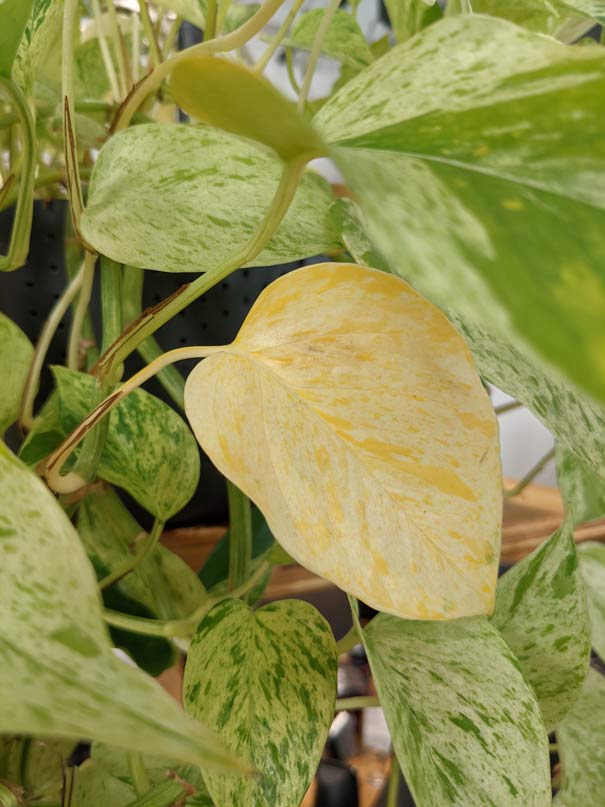
1. Yellowing or Discoloration of Leaves
One of the most common signs of nutrient deficiencies in indoor plants is yellowing or discoloration of leaves. For example, if your plant’s leaves are turning yellow, it may indicate a lack of nitrogen. On the other hand, if the leaves are turning purple or reddish, it could signal a phosphorus deficiency. Pay attention to the color changes in your plant’s leaves to determine which nutrients are lacking.
2. Stunted Growth
If your indoor plant is not growing as quickly as it should, it may be a sign of nutrient deficiencies. Nutrients like potassium and magnesium are essential for promoting healthy growth in plants. If you notice that your plant’s growth has slowed down or stopped altogether, it could be due to a lack of these nutrients.
3. Leaf Curling or Deformation
Another common symptom of nutrient deficiencies in indoor plants is leaf curling or deformation. For example, if your plant’s leaves are curling at the edges or developing unusual shapes, it may indicate a lack of calcium or boron. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of plant cells. Keep an eye out for any abnormalities in your plant’s leaves.
4. Leaf Drop
If your indoor plant is shedding leaves at an alarming rate, it could be a sign of nutrient deficiencies. Potassium and magnesium deficiencies, in particular, can cause leaf drop in plants. Without an adequate supply of these nutrients, your plant may not be able to retain its leaves properly. Monitor your plant for any excessive leaf loss.
5. Poor Flowering or Fruit Production
Nutrient deficiencies can also affect the flowering and fruiting capabilities of indoor plants. For instance, a lack of phosphorus can lead to poor flower formation, while a shortage of calcium can result in underdeveloped fruits. If your plant is not producing flowers or fruits as expected, it may be struggling with nutrient deficiencies.
6. Soil pH Imbalance
In some cases, nutrient deficiencies in indoor plants can be caused by soil pH imbalances. Certain nutrients are only accessible to plants within a specific pH range. For example, iron deficiencies are more common in alkaline soils, while manganese deficiencies are prevalent in acidic soils. Test your soil pH regularly to ensure it is within the optimal range for your plants.
7. Conducting a Nutrient Analysis
If you suspect that your indoor plant is suffering from nutrient deficiencies, consider conducting a nutrient analysis. This involves testing the soil and plant tissue to identify which nutrients are lacking. Based on the results, you can adjust your fertilization routine to address the deficiencies effectively. Consult a gardening expert or professional for assistance with nutrient analysis.
8. Addressing Nutrient Deficiencies
Once you have identified the nutrient deficiencies in your indoor plants, it is essential to take corrective measures promptly. Depending on the specific deficiencies, you may need to adjust your fertilization schedule, switch to a different type of fertilizer, or introduce supplements to provide the necessary nutrients. Regularly monitor your plants’ progress to ensure they are responding positively to the treatment.
Conclusion
Being able to identify and address nutrient deficiencies in indoor plants is crucial for maintaining their overall health and vitality. By observing the signs and symptoms of deficiencies, conducting thorough soil testing, and implementing appropriate corrective measures, you can help your plants thrive and flourish. Remember to provide a well-balanced diet of nutrients to keep your indoor plants happy and healthy!